Standard Deviation = Variance Squared | Standard deviation tells us how spread out a set of numbers (a population) are. The variance of a sampled subset of observations is calculated in a similar manner, using the appropriate notation for sample mean and number of observations. The standard deviation is expressed in the same units as the mean is, whereas the variance is expressed in squared units, but for looking at a distribution, you can use either just so long as you are clear about what you are using. Standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance or in full definition, standard deviation is the square root of the average squared deviation from the mean. So if we take the unsimplified version.
This quantity is known as the standard deviation. That is also true for zero. So if we take the unsimplified version. If they are closer to the mean, there is a lower deviation. We don't really need a formula for that, but let me just give it.

Recall that the variance is in squared units. Deviation just means how far from the normal. Its symbol is σ (the greek letter sigma). These measures are useful for making comparisons between. If they are closer to the mean, there is a lower deviation. Variance and standard deviation are two closely related measures of variation that you will hear about a lot in studies, journals, or statistics class. Standard deviation tells us how spread out a set of numbers (a population) are. The square root of the population variance and. Many people contrast these two mathematical concepts. A low measure of standard deviation. It is therefore more useful to have a quantity which is the square root of the variance. Standard deviation and variance are statistical measures of dispersion of data , i.e., they represent how much variation there is from the average variance is the mean of the squares of the deviations (i.e., difference in values from the mean), and the standard deviation is the square root of that. Two people have correctly pointed out that standard deviation equals variance when both equal 1 because 1 squared equals 1.
The tutorial provides a step by step guide.like us on. Although standard deviation is the most important tool to measure dispersion, it is essential to know that it is derived from the variance. It is therefore more useful to have a quantity which is the square root of the variance. So, this article makes an attempt to shed light on the important difference between variance and standard deviation. The square root of the population variance and.

This quantity is known as the standard deviation. So the more spread out the. Recall that the variance is in squared units. It is the square root of the variance. Standard deviation tells us how spread out a set of numbers (a population) are. For example, a normal distribution with mean = 10 and sd = 3 is. If the points are further from the mean, there is a higher deviation within the date; You need to add the sums and sums of squares of each partition to get the global sum and sum of squares and then use them to calculate the global mean and variance. Standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance by figuring out the variation between each data point relative to the mean. Variance describes, mathematically, how close the observations in a data set (data points) are to the middle of the distribution. √ ( 8.6 ) = 2.93. Standard deviation is a statistical measure of spread or variability.the standard deviation is the root mean square (rms) deviation of the values from their arithmetic mean. With this in mind, statisticians use the square root.
Calculating variance involves squaring deviations, so it does not have the same unit of measurement as the original observations. Unlike, standard deviation is the square root of the numerical value obtained while calculating variance. While variance is a common measure of data dispersion, in similar to the variance there is also population and sample standard deviation. Variance and standard deviation are two closely related measures of variation that you will hear about a lot in studies, journals, or statistics class. If they are closer to the mean, there is a lower deviation.
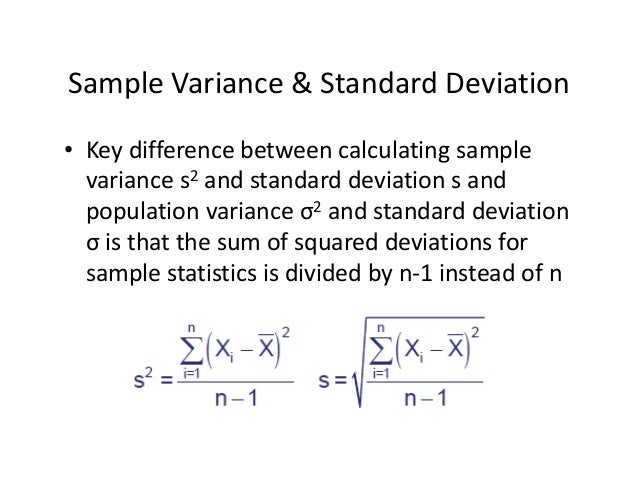
If the points are further from the mean, there is a higher deviation within the date; Many people contrast these two mathematical concepts. Calculating variance involves squaring deviations, so it does not have the same unit of measurement as the original observations. So if we take the unsimplified version. The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out numbers are. It is computed as the average of the squared deviations of the observations from. Two people have correctly pointed out that standard deviation equals variance when both equal 1 because 1 squared equals 1. Add all the squared deviations. This quantity is known as the standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and population standard deviation. The variance of a sampled subset of observations is calculated in a similar manner, using the appropriate notation for sample mean and number of observations. So, this article makes an attempt to shed light on the important difference between variance and standard deviation. Both the standard deviation and variance measure variation in the data, but the standard deviation is easier to interpret.
These measures are useful for making comparisons between standard deviation variance. It is the square root of the variance.
Standard Deviation = Variance Squared: In statistics, the population standard deviation is represented by what we're doing here is we're making use of the idea that the variance is just the standard deviation squared.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar